Concepts and Terms
·

·- 4% Rule: A withdrawal strategy in investing that recommends withdrawing 4% of the accumulated capital annually from a diversified portfolio to ensure a sustainable retirement without depleting the capital.
·
·
·
·
·
·
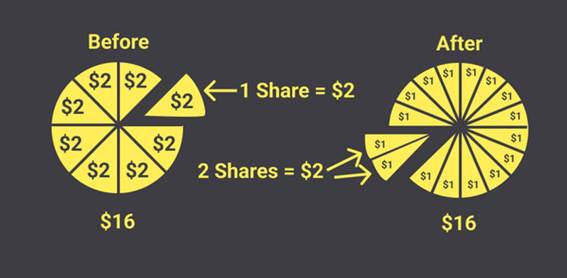
· Stock Split: A process in which a company increases the number of shares in circulation, reducing their price without altering the total value. Example: A 2:1 split doubles the number of shares and halves their price.
·
·
·
·
Markup = (Selling Price - Cost) / Cost × 100
-
-
- Example: A retailer buys a product for $50 and sells it for $75. This means the company is adding a 50% margin over the cost to set the selling price.
(75−50) / 50 × 100 = 50%
- Example: A retailer buys a product for $50 and sells it for $75. This means the company is adding a 50% margin over the cost to set the selling price.
-
·
Markdown = (Original Price - New Price) / Original Price × 100
-
-
- Example: A retailer sells a television for $1,000 but discounts it to $800 during the sales season. This means the price has been reduced by 20% to encourage purchases.
(1000–800) / 1000 × 100 = 20%
- Example: A retailer sells a television for $1,000 but discounts it to $800 during the sales season. This means the price has been reduced by 20% to encourage purchases.
-
·
·-
- Positive covenants: Require the borrower to meet certain requirements (e.g., maintain a minimum level of liquidity or submit periodic financial reports).
- Negative covenants: Prohibit certain actions, such as taking on debt beyond a specified limit or distributing dividends without prior authorization.
- Financial covenants: Related to financial metrics, such as maintaining a debt-to-EBITDA ratio within an allowed range.